Biography of Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru: Early Life, Legacy & Contributions
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table of Content
I. Introduction
A. Early life and education of Pt Jawaharlal Nehru
B. Nehru's role in Indian politics and contribution to Indian history
II. Nehru's Political Career
A. Nehru's involvement in the Indian National Congress
1. Nehru's leadership during the Indian Independence Movement
2. Nehru's role in the drafting of the Indian Constitution
B. Nehru's tenure as India's first Prime Minister
1. Domestic policy initiatives during Nehru's tenure
2. Nehru's contributions to India's foreign policy and non-alignment
III. Nehru's Ideology and Vision
A. Nehru's socialist and secularist beliefs
1. Influence of Marxism and socialism on Nehru's ideology
2. Promotion of secularism and religious tolerance in India
B. Nehru's economic policies and reforms
1. Introduction of the Five-Year Plans in India
2. Emphasis on industrialization and modernization
C. Nehru's contribution to world peace and cooperation
1. Role in the Non-Aligned Movement
2. Nehru's international recognition as a statesman and world leader
IV. Nehru's Legacy
A. Nehru's impact on Indian Independence and nation-building
1. Nehru's role in India's freedom struggle against British rule
2. Nehru's contributions to India's nation-building and development
B. Nehru's influence on Indian democracy and political culture
1. Nehru's contributions to India's democratic institutions
2. Nehru's impact on India's political culture and values
C. Controversies and criticisms of Nehru's policies and leadership
1. Criticisms of Nehru's socialist and economic policies
2. Legacy of Nehru in contemporary India
V. Personal life and Reflections
A. Nehru's family and personal relationships
1. Nehru's marriage and family life
2. Nehru's relationship with his daughter Indira Gandhi
B. Nehru's literary and intellectual pursuits
1. Nehru's authorship of books and writings
2. Nehru's interest in science and education
C. Reflections on Nehru's life and legacy
1. Nehru's impact on Indian and world history
2. Nehru's relevance and significance in contemporary India
VI. Conclusion
A. Summary of Nehru's life and achievements
B. Importance of Nehru's legacy for India and the world
C. Lessons from Nehru's life and leadership
VII. Children's Day
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Table of Content
I. Introduction
A. Early life and education of Pt Jawaharlal Nehru
B. Nehru's role in Indian politics and contribution to Indian history
II. Nehru's Political Career
A. Nehru's involvement in the Indian National Congress
1. Nehru's leadership during the Indian Independence Movement
2. Nehru's role in the drafting of the Indian Constitution
B. Nehru's tenure as India's first Prime Minister
1. Domestic policy initiatives during Nehru's tenure
2. Nehru's contributions to India's foreign policy and non-alignment
III. Nehru's Ideology and Vision
A. Nehru's socialist and secularist beliefs
1. Influence of Marxism and socialism on Nehru's ideology
2. Promotion of secularism and religious tolerance in India
B. Nehru's economic policies and reforms
1. Introduction of the Five-Year Plans in India
2. Emphasis on industrialization and modernization
C. Nehru's contribution to world peace and cooperation
1. Role in the Non-Aligned Movement
2. Nehru's international recognition as a statesman and world leader
IV. Nehru's Legacy
A. Nehru's impact on Indian Independence and nation-building
1. Nehru's role in India's freedom struggle against British rule
2. Nehru's contributions to India's nation-building and development
B. Nehru's influence on Indian democracy and political culture
1. Nehru's contributions to India's democratic institutions
2. Nehru's impact on India's political culture and values
C. Controversies and criticisms of Nehru's policies and leadership
1. Criticisms of Nehru's socialist and economic policies
2. Legacy of Nehru in contemporary India
V. Personal life and Reflections
A. Nehru's family and personal relationships
1. Nehru's marriage and family life
2. Nehru's relationship with his daughter Indira Gandhi
B. Nehru's literary and intellectual pursuits
1. Nehru's authorship of books and writings
2. Nehru's interest in science and education
C. Reflections on Nehru's life and legacy
1. Nehru's impact on Indian and world history
2. Nehru's relevance and significance in contemporary India
VI. Conclusion
A. Summary of Nehru's life and achievements
B. Importance of Nehru's legacy for India and the world
C. Lessons from Nehru's life and leadership
VII. Children's Day
I. Introduction
A. Early life and education of Pt Jawaharlal Nehru
 |
B. Nehru's role in Indian politics and contribution to Indian history
 |
| A young Nehru dressed in a cadet's uniform at Harrow School in England |
II. Nehru's Political Career
A. Nehru's involvement in the Indian National Congress
1. Nehru's leadership during the Indian Independence Movement
2. Nehru's role in the drafting of the Indian Constitution
 |
| Image credit goes to The Quint |
B. Nehru's tenure as India's first Prime Minister
1. Domestic policy initiatives during Nehru's tenure
- Land reforms aimed at redistributing land to farmers
- Introduction of the Five-Year Plans to promote economic growth and development
- Creation of public sector industries to promote self-sufficiency and industrialization
- Investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure to improve the standard of living for all Indians
- Promotion of social welfare policies, such as the abolition of untouchability and the protection of minority rights
2. Nehru's contributions to India's foreign policy and non-alignment
- Promotion of the Panchsheel or Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
- Active involvement in the formation of the Non-Aligned Movement
- Promotion of international cooperation and peaceful resolution of conflicts
- Strong stance against colonialism and imperialism
III. Nehru's Ideology and Vision
A. Nehru's socialist and secularist beliefs
1. Influence of Marxism and socialism on Nehru's ideology
2. Promotion of secularism and religious tolerance in India
B. Nehru's economic policies and reforms
1. Introduction of the Five-Year Plans in India
2. Emphasis on industrialization and modernization
C. Nehru's contribution to world peace and cooperation
1. Role in the Non-Aligned Movement
2. Nehru's international recognition as a statesman and world leader
IV. Nehru's Legacy
A. Nehru's impact on Indian Independence and nation-building
1. Nehru's role in India's freedom struggle against British rule
2. Nehru's contributions to India's nation-building and development
B. Nehru's Influence on Indian Democracy and Political Culture
1. Nehru's Contributions to India's Democratic Institutions
a. Development of a Constitution
b. Establishment of the Election Commission
c. Promotion of Women's Rights
2. Nehru's Impact on India's Political Culture and Values
a. Promotion of Secularism
b. Emphasis on Social Justice
c. Legacy of Democratic Values
C. Controversies and criticisms of Nehru's policies and leadership
1. Criticisms of Nehru's socialist and economic policies
2. Legacy of Nehru in contemporary India
V. Personal life and Reflections
A. Nehru's family and personal relationships
1. Nehru's marriage and family life
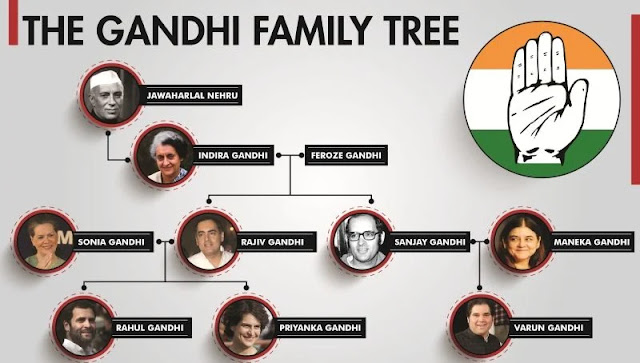
2. Nehru's relationship with his daughter Indira Gandhi
B. Nehru's literary and intellectual pursuits
1. Nehru's authorship of books and writings
2. Nehru's interest in science and education
 |
| 14 November |












Your opinion matters to us!
Please share your thoughts in a respectful and relevant manner and stay on topic.